Department of Cornea & Keratoconus
Diseases affecting the cornea are a major cause of blindness all over the world, second only to cataract in overall importance. A range of infectious and inflammatory eye conditions affect the transparency of the cornea and cause of visual impairment. They add a substantial burden to the community in general and healthcare resources in particular all over the world. Further, individuals with corneal blindness are usually of a younger age group compared with those suffering from cataract. Hence, in terms of total blind years, the impact of corneal blindness is greater.
The cornea department at Shri Aurobindo Nethralaya includes management of corneal and external eye diseases, anterior segment trauma and ocular surface disorders including dry eye, contact lens related eye problems and refractive surgery services. The cornea clinic co-manages ocular conditions by appropriate referral to other departments as well as to other medical specialities as required.
Significant conditions managed in this clinic are Infectious keratitis, Keratoconus, Corneal dystrophies and ocular trauma.
Diagnosis & Treatment
The clinic evaluates and treats patients with cornea and external eye diseases. State-of the-art diagnostic facilities include Corneal topography (Orbscan IIz & Pentacam), Meibography, AS-OCT, Specular microscopy, Ultrasonic pachymetry, and Confocal microscopy. Refractive surgery performed in the department includes Femto laser assisted LASIK, Microkeratome based LASIK and Photorefractive keratectomy.
Routinely performed procedures
-
- Corneal Transplantation
- Penetrating keratoplasty (Optical / Therapeutic / Tectonic / Cosmetic)
-
Lamellar keratoplasty (DSAEK / DSEK / DMEK / DALK)
- Amniotic membrane transplantation
- Pterygium Surgery with Fibrin Glue
- Ocular trauma management
- Refractive laser surgery (LASIK and Wavefront Guided Customized LASIK / PRK and FEMTO LASIK surgery)
- Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation
- Management of Conjunctival tumours
- Keratoprosthesis
- Ocular surface reconstructive surgeries
- Rose K contact lenses and corneal Collagen Cross linking with Riboflavin (C3R) for Keratoconus patients
- Corneal Tattooing
Other Facilities
-
- Eye banking services
- Contact Lens Centre
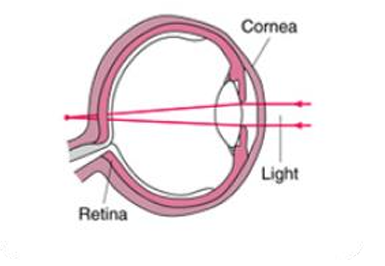
What is Refractive Error?
Normally, the rays of light entering the eye are brought to a precise focus on the retina – the light sensitive layer lining the back of the eye. When such a focus is not achieved, a refractive error results and vision is not clear. These imperfections in the focusing power of the eye are called refractive errors.
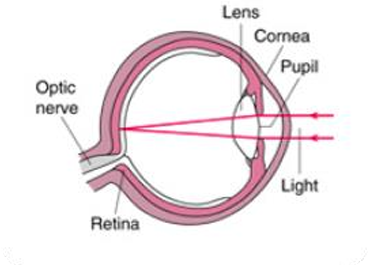
The common refractive errors are
-
- Myopia, or Nearsightedness.
- Hyperopia, or Farsightedness.
- Astigmatism
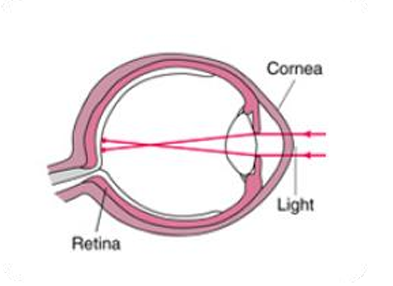
Myopia
A myopic eye is longer than normal or has a cornea that is too steep,
as a
result of
which the light rays focus in front of the retina. Close objects look
clear,
but distant
objects appear blurred.
Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
Hyperopia is a term used to describe the condition of farsightedness.
The
causes of
hyperopic are typically genetic and involve an eye that is too short or
a
cornea that is
too flat, as a result of which images are focused at a point behind the
Retina.
People
with hyperopia can usually see distant objects well, but have trouble
focusing
on
nearby objects

Astigmatism (Distorted vision)
Astigmatism (cylindrical error) occurs when the incoming light rays are
unable
to reach
a common point of focus within the eye. Astigmatism distorts or blurs
vision
for both
near and far objects. The cornea is the clear front window of the eye.
When you
have
astigmatism, the cornea curves more in one direction than in the other,
like a
rugby
ball. It is possible to have astigmatism in combination with myopia or
hyperopia.